Non-Volatile Flash Memory Device Based on a Hexagonal Boron Nitride Thin Film
- admin
- 2022-08-22
- 7963
Research Team Led by Prof. Park Hamin (Dept. Of Electronic Engineering, Kwangwoon University) Developed a Non-Volatile Flash Memory Device Based on a Hexagonal Boron Nitride Thin Film
- Published in JCR Applied Physics Q1 Journal
-
- Controlling write and erase operations of
non-volatile flash memory using the energy bandgap control of the hexagonal
boron nitride thin film -
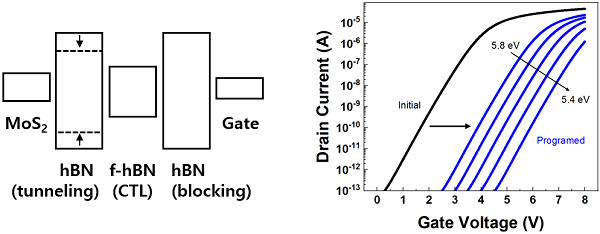 ?
?
Professor Ha-Min Park (Department of
Electronic Engineering) of Kwangwoon University and Professor Byung-Cheol Jang
(School of Electronics Engineering) of Kyungpook National University proved
that hexagonal boron nitride among new materials can be used as a charge
storage layer. They verified it through TCAD (Technology computer-aided design)
simulation.
Flash memory is a non-volatile memory used in
most IT devices, such as servers, PCs, tablets, and smartphones, and plays a
role in storing information. Current flash memory devices use a thin film
material composed of a silicon oxide film, a nitride film, and an oxide film as
a charge storage layer. The threshold voltage of the element changes according
to the stored charges. By applying a new material rather than silicon material
to these flash memory devices, the research team developed a device that can
store more information in less space and operate faster.
This research was carried out with the support
of the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Ministry of Education,
BK-21, key research institutes, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and
Kwangwoon University. The research results were published in the professional
journal Surfaces and Interfaces (JCR Applied Physics field Q1, IF: 6.137) in
July 2022. It was published in the online edition under the title “Non-volatile
flash memory based on Van der Waals gate stack using bandgap tunability of
hexagonal boron nitride”.
*Research link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102179