Eco-friendly Nanogenerator: High-power Electricity from Daily Life
- admin
- 2024-07-03
- 1176
Professor Jaeyoung Park's Research Team (Electronic Engineering) Develops an Eco-friendly Nanogenerator Producing High-power Electricity from Daily Life
- Development of High-output Triboelectric Nanogenerator and PEO@Poly-DADMAC Composite Nanofibers with High Cationic Properties -
- Application to Wearable Medical/Healthcare, Soft Robots, Electronic Skin, Human-Machine Interface Power-free Pressure Sensors, and Eco-friendly Power Sources -
- Published as a Cover Paper in the Internationally Renowned Journal, Advanced Functional Materials by Wiley (IF:18.8) -
The research team of Professor Jaeyoung Park from the Department of Electronic Engineering at Kwangwoon University has synthesized Poly-DADMAC (Polydiallyldimethylammonium Chloride) and PEO (Polyethylene Oxide) polymer electrolytes, applied electrospinning technology, and developed composite nanofiber materials with very high electric positivity for the first time in the world. Using these materials, they successfully developed a high-output wearable triboelectric nanogenerator and power-free pressure sensors.
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT under the National Research Foundation's Mid-Career Researcher Support Program (NRF-2020R1A2C2012820) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy's Industrial Technology Innovation Program (RS-2022-00154983, Development of Autonomous Power Sensor Platform for Low-power Sensors and Actuators). The research results were published in Advanced Functional Materials (IF: 18.8), the world's leading journal in functional materials and devices, by Wiley. (https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202403899)

Professor Jaeyoung Park from the Department of Electronic Engineering at Kwangwoon University and Ph.D. student M. Robiul Islam (starting from left in the photo)
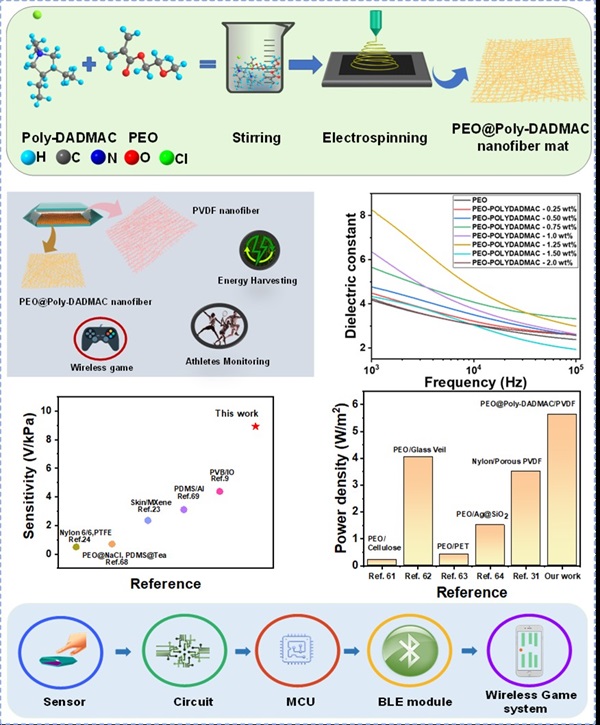
Performance characteristics of high-output triboelectric nanogenerators and power-free pressure sensors based on PEO@Poly-DADMAC composite nanofibers using electrospinning.